Discover the Top 8 Differences Between B2B and B2C Marketing

Here are the top eight ways B2B and B2C marketing are different:
Audience size and focus
Who makes decisions
Buying cycle length
Motivation behind purchases
Messaging style
How personalisation works
Value and cost
Relationship type
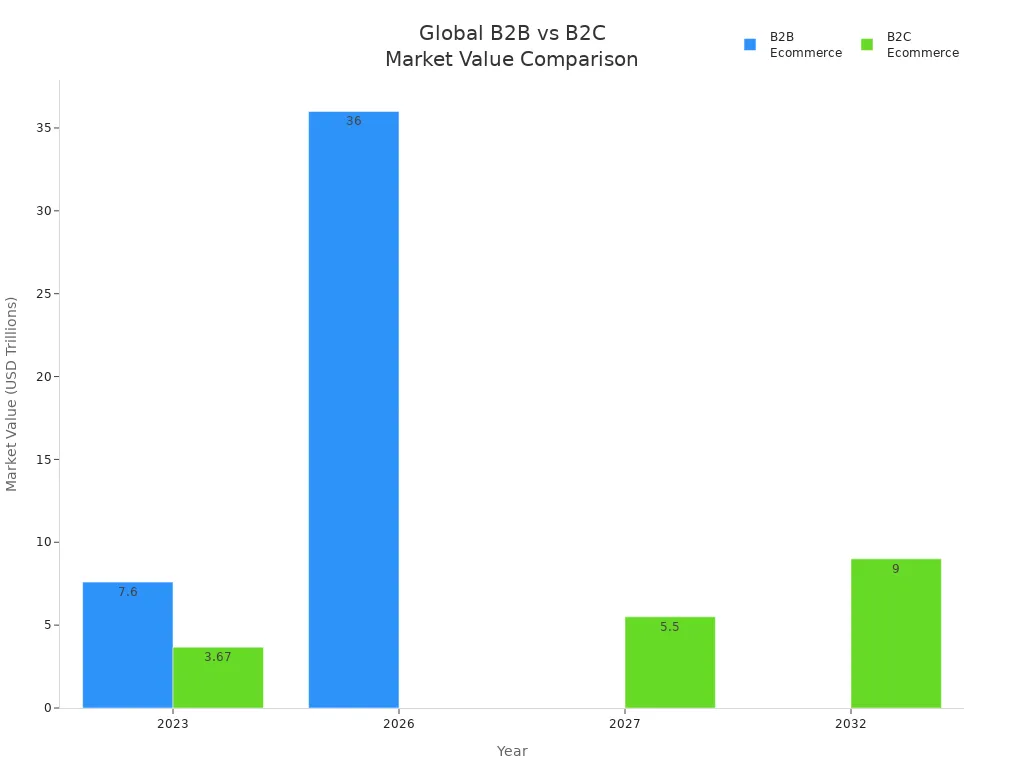
You can see how large these sectors are in the chart below. The global B2B ecommerce market will reach $36 trillion by 2026. This is much bigger than B2C, which will reach $9 trillion by 2032.
Marketers see that B2B Marketing works best with long-term value. B2C works better with fast, emotional messages. Here’s a quick comparison:
Aspect | B2B Marketing Strategy Characteristics | B2C Marketing Strategy Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Target Audience | Smaller, specific group of business decision-makers | Larger, diverse consumer base |
Decision-Making Process | Complex, multi-stakeholder, logical, ROI-driven | Quicker, individual or small group, emotional and immediate benefits |
Customer Relationships | Long-term, personalised, relationship-focused | Short-term, broad, mass market oriented |
Research Methodologies | Customised qualitative methods | Mixed quantitative and qualitative methods |
Data Sources | Niche industry reports, proprietary data | Abundant consumer data from social media, surveys |
Market Segmentation | Industry-specific sectors, company size | Demographic, psychographic, behavioural segmentation |
Use of Technology | Advanced analytics and AI for industry data | Advanced analytics and AI for broad consumer data |
Marketing Focus | Long-term value, ROI, business needs | Consumer preferences, trends, immediate satisfaction |
Key Takeaways

B2B marketing talks to small groups of business people. B2C marketing talks to many different customers. Business buying needs many people to agree. It can take months to decide. Consumers buy things fast and often alone. B2B buyers care about facts, value, and long-term gains. B2C buyers care more about feelings and quick happiness. B2B messages are formal and have lots of details. B2C messages are simple, emotional, and easy to share. B2B personalisation means making content fit jobs and industries. B2C personalisation is about what people like and do. B2B sales are big, special deals with help after buying. B2C sales are smaller, normal products sold quickly. B2B wants long partnerships with clients. B2C wants fast sales and happy customers. Using the right marketing plan for your audience helps you do better. It also makes your relationships stronger.
Audience

B2B Marketing Audience
Business Buyers
When you market to businesses, you talk to a small group. These people are professionals who decide for their companies. You might aim at procurement managers or IT directors. Sometimes, you target C-level executives too. Each person has a job and business goals. They want answers to real problems. They need value for their organisation. You must show how your product helps their business.
B2B Marketing often focuses on special industries. These include virtual and augmented reality, medical marijuana, and financial technology. Biotechnology and content marketing are also common. These fields have special needs and problems. Your audience wants you to know their industry. They expect you to use their language. They want good reasons to buy, not just cool adverts.
Smaller Segments
B2B audiences are much smaller than consumer ones. You may only have hundreds or thousands of buyers. You cannot use mass marketing here. You need to use careful segmentation. You look at company size and industry. You check annual turnover and job titles. You might use firmographic data or intent signals. This helps you find the right people.
Tip: If you know more about your audience’s business, you can make your message better and stand out.
Here’s a table to show the main differences:
Characteristic | B2B Marketing Audiences | B2C Marketing Audiences |
|---|---|---|
Target Audience Composition | Companies, organisations, professionals | Individual consumers |
Decision-Making Process | Multiple stakeholders, longer evaluation | Single decision-maker, quick decisions |
Sales Cycle | Longer (months to a year) | Shorter (minutes to days) |
Buying Motives | Rational, ROI-focused | Emotional, personal needs |
B2C Audience

Individual Consumers
When you market to consumers, you talk to individuals. These people buy for themselves or their families. They care about their own needs and wants. You might split them by age or location. You could use income or hobbies too. Their choices are quick and based on feelings. They want things that make life easier or more fun.
Larger Markets
B2C audiences are very large. You could have millions of customers. This means you use wide segmentation. You look at demographics and psychographics. You check buying behaviour too. You might group people by age or gender. You could use lifestyle or shopping habits. Your marketing must reach many people. So, your messages are simple and clear.
B2C segmentation uses personal data like age, location, income, and likes.
B2B segmentation uses business data like company size, industry, and job roles.
You can see that audience size and segmentation change your marketing style. In B2B Marketing, you focus on a small group and get personal. In B2C, you try to reach as many people as you can.
Decision-Makers

Multiple Stakeholders
Group Decisions
When you sell to businesses, you do not talk to just one person. You deal with a group. Each person has a job and their own ideas. They work together to decide if your product is good for them. You might speak to a technical expert or a finance manager. Sometimes, you talk to the person who will use the product. Each person thinks about your offer in a different way.
Here are some common roles in a B2B buying group:
Role | What They Do | When They Get Involved |
|---|---|---|
Initiator | Finds the need and starts the process | At the very start |
Buyer | Looks after the money and paperwork | Throughout the process |
Decision Maker | Makes the final choice on what to buy | Selection and earlier stages |
Coordinator/Gatekeeper | Decides who can speak to the decision-makers | All the way through |
Influencer | Gives advice and shares opinions | Early and middle stages |
User | Uses the product and gives feedback | Middle and end of the process |
You may also meet champions, budget owners, technical experts, and ratifiers. Each person helps move the deal forward or can slow it down.
Approval Chains
Buying in B2B takes a long time. This is because many people must say yes at each step. A B2B buying group often has five to ten people. Each one checks if your product is right for them. This makes things slower and harder.
Here is what happens in a normal B2B approval chain:
More people join in as the deal gets bigger.
Teams like finance, IT, and operations want to help decide.
Each team checks for risks, costs, and benefits.
The process can go back and forth as people ask for more details.
Contracts, ROI reports, and risk checks add more steps.
Digital tools can help, but rules can still slow things down.
You must keep everyone updated and answer many questions. If you miss one person’s worry, the deal can stop. So, you need to build trust and show value to every person.
Single Buyer

Personal Choice
When you sell to consumers, you usually talk to one person. This buyer chooses for themselves or their family. They do not need to ask a group or get approval from others. Their choice is quick and based on what feels right.
In B2C, you see:
One or two people making the choice.
Fast choices, sometimes in minutes or hours.
Choices made by feelings, needs, or a sudden want.
You can see the difference in this table:
Aspect | B2C Purchase Decision | B2B Purchase Decision |
|---|---|---|
Number of Decision Makers | 1-2 individuals | |
Decision Speed | Hours to days | 3-6+ months |
Decision Drivers | Emotions, desires, brand connection | ROI, efficiency, cost savings |
Content Preference | Visual, simple, emotional | Detailed, information-rich |
Motivation | Convenience, status, impulse | Metrics, consensus, risk management |
B2C buyers do not only use feelings. In B2B, feelings matter too. A manager may worry about their reputation or want to make a smart choice. Still, B2C is much simpler. You can focus on how your product helps the buyer. You do not need to worry about a long approval chain.
Tip: If you know who decides, you can change your message to fit them—whether it is a group or just one person.
Buying Cycle

B2B Marketing Cycle
Longer Process
When you work in B2B Marketing, you face a much longer buying cycle. You do not just talk to one person. You deal with a group. Each person checks your offer and asks questions. The process can take six to eight months, sometimes even longer. You need to be patient and keep everyone informed.
Here’s a table to show the main differences in buying cycles:
Buying Cycle Type | Average Length | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
B2B | Many stakeholders, complex decisions, lots of research and approvals | |
B2C | Shorter, often impulsive | Few decision-makers, quick and simple purchases |
You might wonder why B2B takes so long. The answer is simple. Businesses want to avoid mistakes. They spend their company’s money, so they check every detail. They want to see the value and make sure your product fits their needs.
Complex Steps
The B2B buying cycle has many steps. You cannot skip any of them. Here’s what usually happens:
Someone in the company spots a problem or need.
The team defines what they want and agrees to buy.
They look for solutions and do research.
They pick a supplier and make a choice.
They justify the decision and get approvals from managers.
After buying, they review the product and build a relationship with you.
Each step involves different people. You might talk to decision-makers, influencers, users, and even finance teams. On average, seven people join the process. Some studies say it can be as many as thirteen. This makes the process slow and detailed.
Tip: If you want to win in B2B Marketing, you must guide each person through these steps. Give them the right information at the right time.

B2C Cycle
Shorter Path
B2C buying cycles move much faster. You usually talk to one person. This person buys for themselves or their family. They do not need to ask a group or wait for approvals. Most purchases happen in minutes or days.
Here’s a table to compare the two cycles:
Metric | B2B Buying Cycle | B2C Buying Cycle |
|---|---|---|
Average Duration | 6–8 months | Minutes to days |
Number of Decision Makers | 7 (average) | 1 |
Purchase Complexity | High | Low |
Quick Decisions
You see quick decisions in B2C because people buy on impulse. They see a product, like it, and buy it. Marketers use urgency tactics, such as limited-time offers, to push people to act fast. This leads to higher conversion rates. You can sell more in less time.
B2C purchases are simple and fast.
B2B purchases are slow and complex.
If you sell to consumers, focus on making the buying process easy. Use clear calls to action and simple steps. If you sell to businesses, prepare for a longer journey. Build trust and help each person in the group feel confident about the decision.
Motivation

Logic-Driven
ROI Focus
In B2B Marketing, buyers want proof before buying. They look for a clear return on investment. Every purchase must help the business in some way. You need to show how your product saves money or solves problems. Buyers often ask for data and case studies. They want to see numbers before they agree.
Trust and reputation are very important. If other companies trust you, buyers feel safer. Many buyers check testimonials and case studies first. They want to feel sure your solution works.
Business Needs
Business buyers do not shop for fun. They have a job to do at work. Their main goal is to solve a problem. You must know what worries them most. Maybe they want to save time or reduce stress. They might want their team to work better. If your product helps with these goals, you stand out.
Here are some logical things that affect B2B choices:
Trust and credibility – Buyers want to work with known companies.
Data-driven decisions – They spend time comparing options.
Social proof – Reviews and case studies help them feel safe.
Value and ROI – They look for long-term gains, not just quick wins.
Fear can also matter. Buyers want to avoid mistakes at work. Money-back guarantees or strong support can help them worry less.
Here’s a table to show the main differences in motivation:
Motivation Aspect | B2B Buyers (Business-to-Business) | B2C Buyers (Business-to-Consumer) |
|---|---|---|
Primary Drivers | Rational factors: logic, ROI, problem-solving, long-term value | Emotional factors: personal satisfaction, impulse buying, brand loyalty |
Emotional Role | Trust, confidence, reputation, peace of mind influence decisions | Strong emotional fulfilment, social influence, impulse decisions |
Value Definition | Cost efficiency, customisation, expertise, dependability | Emotional and personal benefits, convenience, brand trust |
Relationship Focus | Long-term partnerships, multiple stakeholders, trust building | Shorter, more transactional, emotional connection |
Decision Cycle | Longer sales cycles, extensive research and evaluation | Shorter sales cycles, quicker decisions |
Social Influence | Acceptance via case studies and testimonials | Peer pressure, social media, online reviews |
Emotion-Driven

Personal Interests
When you market to consumers, you use feelings. People buy things to feel happy or proud. Emotions like joy and trust can make people buy. You might use stories or pictures that make people dream. If your product makes life easier or more fun, people like it.
Emotional appeal is strong. It helps you connect with buyers fast. People remember how your brand made them feel.
Impulse Buys
Consumers often buy things quickly. They see something they like and buy it right away. You can use urgency, like “limited-time offers”, to make them act fast. Social proof, like reviews, also helps. People want to try what others love.
Emotional triggers like fear of missing out and excitement push fast choices.
Social media and friends can affect what people buy.
In B2C, you help people feel good and buy quickly. In B2B Marketing, you build trust and show value over time. Both logic and emotion matter, but you use them differently for each group.
Messaging

B2B Marketing Messaging
Formal Tone
When you talk to business buyers, you must sound professional. You use clear words and do not use slang. Your language shows respect and helps build trust. Business clients want to know you understand their field. They look for facts, not just big claims. You write in a calm and logical way. This makes you seem trustworthy and steady.
Tip: To stand out, try being real on trusted platforms. Dell Technologies used humour and fun posts on Reddit. This made their brand more trusted and liked. You can use humour, but it should be smart and fit the topic.
Detailed Content
Business buyers want lots of details. They read whitepapers, case studies, and expert talks. You must give them proof and data. They want to see how your product fixes their problems. You might share reports or show return on investment. Your content should answer hard questions and help buyers choose well.
Here’s a table to show the main differences in messaging:
Aspect | B2B Messaging | B2C Messaging |
|---|---|---|
Tone | Professional, logical, informative | Relatable, conversational, emotional |
Content Detail | Detailed: whitepapers, case studies, industry reports, expert interviews | Visually appealing, shareable, product demos, lifestyle articles, promotions |
You can use many channels for your campaigns. Amazon Business made a campaign with special content and stories. This helped them reach more people and made their brand stronger. If you want to make your messaging better, try these ideas: Use LinkedIn for getting noticed and retargeting. Match your content to each step of the buyer’s journey. Mix helpful and sales content. Work with industry experts for social proof. Use video to explain hard ideas.

B2C Messaging
Emotional Appeal
When you talk to consumers, you want them to feel something. You use stories, pictures, and catchy lines. Your goal is to connect with their feelings. People buy things that make them happy or fix a problem fast. You can use humour, excitement, or make them feel they must act now. This helps you get their attention and quick choices.
B2C messaging shows benefits that make life better.
You want your message to be easy to remember and share.
Simplicity
Keep your words short and clear. Consumers do not want long details. They want to know what your product does and why it matters. Use short sentences and clear calls to action. Show the value right away. You can use product demos, lifestyle pictures, or quick deals.
Note: B2C messaging works best when you match your message to what people want now. Use emotional triggers and make it easy for them to say yes.
You can see that B2B Marketing needs a formal and detailed style. B2C messaging uses feelings and keeps things simple. If you match your style to your audience, you will get better results.
Personalisation

Role-Based
Industry Focus
In B2B Marketing, you must know each industry well. You cannot send the same message to every business. Each company has its own way of talking and its own problems. If you use their special words, they trust you more. This shows you understand their work.
You might speak to a finance manager in banking. Or you could talk to an IT director in healthcare. Each job cares about different things. You need to talk about their own problems. For example, a compliance officer wants to know about rules. A sales manager wants to see how your product helps them earn more.
Almost 75% of business buyers want you to make your message personal before they buy. If you do this, you start building trust early.
Custom Solutions
You cannot give every business the same answer in B2B Marketing. You need to make special demos and pages for each company. This shows you care about what they need. You might use account-based marketing for big clients. This means you send special offers to each business.
Here are some ways to make things personal for B2B clients:
Use case studies and stories from their industry.
Talk about problems like rules, saving time, or growing.
Give choices for payments and special packages.
Offer a manager just for them and help them get started.
A table can help you see the difference:
Approach | B2B (Role-Based) | B2C (Behaviour-Based) |
|---|---|---|
Focus | Job role, industry, company needs | Personal interests, habits |
Content | Custom demos, tailored presentations, ABM | Product suggestions, dynamic feeds |
Relationship | Long-term, trust-building | Quick, emotional connection |

Behaviour-Based
Interests
In B2C, you look at what people like and do. You watch what they look at, buy, and share. This helps you show them things they might want. For example, if someone looks at trainers, you show them more sports gear.
You use data from social media and website visits. You also use what they have bought before. This helps you make special offers or show new products they might like.
B2C personalisation is quick and simple. You want people to buy fast and feel happy.
Preferences
You also check what brands or colours people like. You can change your website or emails to match these likes. This makes shopping easier and more fun.
In B2B, you can use behaviour-based signs too. You might see which articles a buyer reads or which webinars they join. This helps you send the right message at the right time. Smart tools use AI to make this easy and fast.
77% of B2B buyers will not read content that does not fit their interests or where they are in the buying process. If you use both role-based and behaviour-based data, you can get more people interested and win more deals.
Personalisation is not just something extra. It is needed if you want to stand out and make real connections, whether you sell to businesses or people.
Value and Cost

High Stakes
Larger Investments
When you sell to businesses, you deal with much bigger numbers. You might see a single order worth thousands or even hundreds of thousands of pounds. According to a UNCTAD report, B2B e-commerce payments reached about $25 trillion, while B2C only hit $4.4 trillion. That’s a huge gap. It means each business deal is often much larger than a typical consumer sale. Allianz Trade also points out that buyer credit limits in B2B Buy Now Pay Later deals can go over $100,000. So, you need to treat every business sale as a big event.
You can’t rush these deals. Businesses want to know exactly what they’re getting for their money. They ask for proof, case studies, and sometimes even a demo. You need to show them the value, not just the price. If you help them see how your product saves money or boosts profits, you’ll have a better chance of closing the deal.
Customisation
Business buyers rarely want a one-size-fits-all solution. They expect you to tailor your offer to their needs. You might need to adjust features, payment terms, or even the way you deliver your service. Customisation helps you stand out and builds trust. When you listen to what a business wants and make changes just for them, you show that you care about their success.
Tip: Always ask your business clients what matters most to them. This helps you create a package that fits their goals and makes your offer more valuable.
Lower Stakes
Standard Products
When you sell to consumers, things look very different. Most people buy standard products off the shelf. They don’t ask for special features or custom deals. You can sell the same item to thousands or even millions of people. This makes your job easier, but it also means you need to stand out in a crowded market.
People want to know what your product does and why it’s better than others. You need to make your message clear and simple. If you can show how your product fits into their daily life, you’ll grab their attention.
Price Sensitivity
Consumers care a lot about price. They often compare brands and look for the best deal. If your price is too high, they might walk away. This is why you see so many discounts, bundles, and special offers in shops and online. B2C customers are quick to react to sales and promotions. They want to feel like they’re getting good value for their money.
B2C marketing focuses on quick sales, emotional appeal, and price promotions.
You need to highlight value, emotional benefits, and competitive pricing.
B2C buyers often make decisions on impulse, so your offer needs to stand out fast.
In contrast, business buyers are less sensitive to price. They care more about long-term value and how your product solves their problems. They want detailed information and proof, not just a low price. You’ll spend more time building a relationship and showing how your product fits their business goals.
Here’s a quick table to compare:
Aspect | Business Buyers (High Stakes) | Consumers (Lower Stakes) |
|---|---|---|
Average Deal Size | Much larger (££££–£££££) | Smaller (£–£££) |
Customisation | Expected | Rare |
Price Sensitivity | Lower | Higher |
Decision Drivers | Value, ROI, custom fit | Price, emotion, convenience |
Note: If you understand what your buyers value most, you can adjust your offer and messaging to win more sales—whether you’re selling to businesses or consumers.
Relationships

Long-Term
Partnerships
When you work with business clients, you build real partnerships. You do not just sell a product and walk away. You get to know your client’s business. You learn what matters to them. You help them reach their goals. This partnership can last for years. You become a trusted adviser, not just a supplier.
In business, most of your revenue comes from clients you already know. In fact, 72% of business revenue comes from existing customers. These clients can bring in up to 95% more revenue over time. It costs much less to keep a client than to find a new one. If you focus on building strong partnerships, you will see your business grow.
Ongoing Support
Ongoing support is the heart of a strong business relationship. You do not just answer questions when something goes wrong. You check in with your clients. You offer new ideas and solutions. You help them use your product better. You might even train their team or share tips to help them succeed.
You keep in touch with personalised messages.
You offer help before problems appear.
You give updates and new features to keep things fresh.
You make sure your client feels valued and supported.
Customer Success teams play a big role here. They help your clients reach their goals. They make sure your product keeps delivering value. This support builds trust and loyalty. Your clients stay longer and are less likely to leave. You create a partnership that grows stronger every year.
Characteristic | B2B Relationships | B2C Relationships |
|---|---|---|
Long-term partnerships with recurring revenue | Typically transactional, short-term | |
Retention focus | Continuous engagement, proactive support, innovation | Repeat purchases, immediate satisfaction |
Product/service complexity | High, customised, requiring ongoing support | Generally standardised, less complex |

Transactional
One-Time Sales
When you sell to consumers, most relationships are short. You sell a product, and the sale is done. The buyer might come back, but you do not expect it. You focus on making each sale quick and easy. You want the buyer to feel happy right away.
Most consumer sales are one-off purchases.
You do not need to know the buyer’s long-term goals.
You use promotions and discounts to encourage quick decisions.
You focus on satisfaction in the moment.
In consumer sales, you do not spend much time on ongoing support. If a buyer has a problem, they might contact customer service. After that, the relationship usually ends. You do not build deep partnerships. You aim for high volume and fast sales.
Remember: In business sales, you build long-term trust. In consumer sales, you focus on quick wins.
You’ve seen that B2B and B2C marketing are worlds apart. Here are the eight main differences:
Target audience
Buyer motivations
Marketing funnel
Decision making
Relationship building
Advertising approach
Purchasing habits
Buying cycle
If you match your strategy to your market, you’ll see better results. Many brands grow faster and build stronger relationships when they adapt their approach. Take a moment to review your own marketing. Are you using the right tactics for your audience? Now’s the time to put these insights into action and watch your results improve.

FAQ
What is the biggest difference between B2B and B2C marketing?
You focus on businesses in B2B and individuals in B2C. B2B needs longer relationships and detailed information. B2C works best with quick, emotional messages. The way you talk and sell changes a lot between the two.
Do B2B buyers care about price as much as B2C buyers?
B2B buyers look at value and long-term benefits. They want to see how your product helps their business. B2C buyers often care more about price and special offers. You need to show value in both, but in different ways.
How long does a typical B2B buying cycle last?
A B2B buying cycle can last from a few months to over a year. You deal with many people and steps. In B2C, buyers often decide in minutes or days. Patience and follow-up matter in B2B.
Can I use the same marketing message for both B2B and B2C?
No, you should not. B2B buyers want facts, proof, and a professional tone. B2C buyers like simple, emotional messages. If you match your message to your audience, you get better results.
Why is personalisation important in B2B marketing?
Personalisation shows you understand your client’s business. You build trust and stand out from competitors. Custom offers and industry-specific content help you win more deals. In B2C, personalisation makes shopping feel special and fun.
What channels work best for B2B marketing?
You get the best results with LinkedIn, email, and industry events. These channels help you reach decision-makers. For B2C, social media, TV, and online ads work well. Choose channels that fit your audience.
How do relationships differ in B2B and B2C?
In B2B, you build long-term partnerships and offer ongoing support.
In B2C, most sales are quick and transactional.
You need to focus on trust and service for B2B, but speed and satisfaction for B2C.
TangBuy: A Smarter Way to Dropship in 2025
If you're looking to stay competitive with dropshipping in 2025, speed and trend-awareness are key. TangBuy helps you stay ahead with real-time product trends, fast fulfilment, and factory-direct sourcing. With over 1 million ready-to-ship items, 24-hour order processing, and seamless Shopify integration, TangBuy makes it easier to test, scale, and succeed in today's fast-moving eCommerce landscape.
See Also
Choosing Between BigCommerce And Shopify For eCommerce Success
Comparing BigCommerce And Shopify Platforms For 2025 eCommerce
Best Eight Free Apps To Sell Online And Earn In 2025
Dropshipping Or Amazon FBA Which Model Yields Higher Profits
Five Effective Ways To Source Dental Products For Online Stores

